Longest path in a network
Quido is currently evaluating the performance of various campus networks around the country. A network is a tree structure made of servers, also called nodes, and cable connections between them. The quality of the network depends on the speed at which the messages can be transmitted through the network. The time of travel along the cables is negligibly small and Quido considers it being zero in all cases.
Each server is characterized by single number which is equal to the number of microseconds required to process the message and -- if needed -- send it to the next server.
The network quality is equal to the longest possible time in which a message can be propagated through the network. In other words, it is the maximum possible sum of characteristics of all servers on a path from some server to some other server in the campus.
For simplicity reasons, Quido keeps the description of each network in a specific string format which we describe bellow.
A network contains one distinctive node called the root. Let x and y be two nodes. Node y is called descendant of x if x lies on the path connecting y and the root. Node y is called child of x if x and y are connected directly by cable and y is descendant of x. Part of the network containg node x, all its descendants, all cables between them and no other nodes or cables is called a subnetwork with root x.
Note that each node, including the network root, is a root of some subnetwork.
To describe the network a string of symbols is constructed recursively.
-
1. A subnetwork containing only one node with characteristic
cis described by the string(c). -
2. Let s1, s2, s3, ..., sk (k > 0) be all the subnetworks which roots are children of node x, let
d1, d2, d3, ..., dkbe the respective descriptions of those subnetworks.
The description of subnetwork with root x is the string(cd1d2d3...dk), wherecis the characteristic of x.
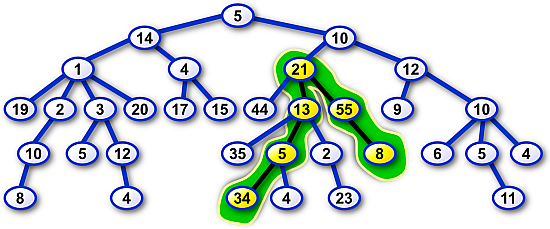 Image 1. Example of a network which quality is 136. The path with maximum sum of server characteristics (equal to 136) is highlighted. The root is the topmost node in the picture. The network is described by the string (5(14(1(19)(2(10(8)))(3(5)(12(4)))(20))(4(17)(15)))(10(21(44)(13(35)(5(34)(4))(2(23)))(55(8)))(12(9)(10(6)(5(11))(4))))). |
The task
Given the network description in the Quido's format find the quality of the network.
Implementation note
Quido's wiew is that the effective solution of the task should be also memory efficient. In fact, he is convinced that the input string description is sufficient to perform all necessary calculations and that there is no need to build other internal representation of the entire network.
Input
The input contains one text line containing the network description in Quido's format. There are no other symbols on the line. All node characteristics are positive integers smaller than 100. There is at least one node and no more than 5×106 nodes in the network.
Output
The otuput contains one text line with one integer representing the quality of the network.
Example 1
Input(5(14(1(19)(2(10(8)))(3(5)(12(4)))(20))(4(17)(15)))(10(21(44)(13(35)(5(34)(4))(2(23)))(55(8)))(12(9)(10(6)(5(11))(4)))))Output
136The network is depicted in the Image 1 above.
Example 2
Input(4(3(2(3)(5)(1)(6))))Output
15
Example 3
Input(8(4(2(1)(3))(6(5)(7)))(12(10(9)(11))(14(13)(15))))Output
66
Public data
The public data set is intended for easier debugging and approximate program correctness checking. The public data set is stored also in the upload system and each time a student submits a solution it is run on the public dataset and the program output to stdout and stderr is available to him/her.
Link to public data set