Color Graph II
Let us associate each node of a simple undirected graph with some color. We say that a triple of nodes is a triangle if any pair of these three nodes is connected by an edge. We say that a triangle is a chromatic triangle if the colors of its three nodes are all different. A distance between a triangle T and a node u in the graph is equal to the minimum possible length of a path which connects u to some node in T. In this problem, one prominent node, called base node, is specified in the graph.
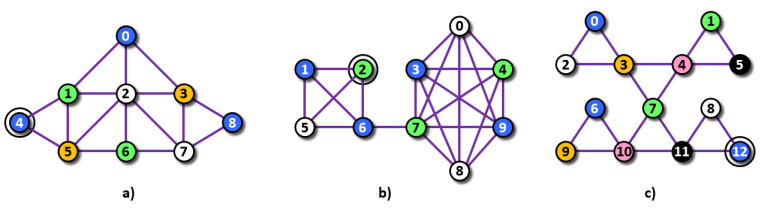 Image 1. Three graphs corresponding to Example 1, 2, and 3 below. Each base node is highlighted by an additional circle. For each graph we specify a distance from the base node and the list of chromatic triangles in that distance. a) Distance 0: (1, 4, 5); distance 1: (0, 1, 2), (1, 2, 5), (2, 5, 6); distance 2: (0, 2, 3); distance 3: (3, 7, 8). b) Distance 0: (1, 2, 5), (2, 5, 6); distance 2: (0, 3, 7), (0, 7, 9), (3, 7, 8), (7, 8, 9); distance 3: (0, 3, 4), (0, 4, 9), (3, 4, 8), (4, 8, 9). c) Distance 0: (8, 11, 12); distance 1: (7, 10, 11); distance 2: (3, 4, 7), (6, 9, 10); distance 3: (0, 2, 3), (1, 4, 5). |
Â
The task
You are given a graph, a color of each its node and a base node in the graph. Determine the distances from the base node to all chromatic triangles in the graph.
Input
The first input line contains four integers N, E, C, S separated by space and representing (in this order) the number of nodes in the graph, the number of edges in the graph, the number of node colors in the graph and the base node label.
We assume that the nodes are labeled 0, 1, ..., N−1.
The next line contains N integers, separated by spaces, which represent the list of colors of particular nodes. The colors are listed in ascending order of node labels. The first integer represents the color of node 0, the second integer represents the color of node 1, etc. We assume that the colors are labeled 0, 1, ..., C−1.
Next, there are N −1 text lines, each specifies one edge in the graph. The line contains two integers, separated by space, which represent the labels of the edge endnodes. The edges are listed in no particular order.
It holds, 2 ≤ N ≤ 104, 3 ≤ E ≤ 105, 3 ≤ C ≤ 100. The input graph contains at least one chromatic triangle.
Output
The output contains one or more lines. Each line contains two values d, f separated by space. Value f is the number of chromatic triangles in the graph which distance from the base node is exactly d. If f equals 0 the line is not printed. The lines are sorted in ascending order of d values.
Example 1
Input9 16 4 4 0 1 2 3 0 3 1 2 0 0 1 0 2 0 3 1 2 1 4 1 5 2 3 2 5 2 6 2 7 3 7 3 8 4 5 5 6 6 7 7 8Output
0 1 1 3 2 1 3 1The graph in Example 1 is depicted in Image 1 a).
Example 2
Input10 22 3 2 2 0 1 0 1 2 0 1 2 0 1 2 1 5 1 6 2 5 2 6 5 6 6 7 0 3 0 4 0 7 0 8 0 9 3 4 3 7 3 8 3 9 4 7 4 8 4 9 7 8 7 9 8 9Output
0 2 2 4 3 4The graph in Example 2 is depicted in Image 1 b).
Example 3
Input13 18 6 12 0 1 2 3 4 5 0 1 2 3 4 5 0 0 2 0 3 1 4 1 5 2 3 3 4 4 5 3 7 4 7 6 9 6 10 7 10 7 11 8 11 8 12 9 10 10 11 11 12Output
0 1 1 1 2 2 3 2The graph in Example 3 is depicted in Image 1 c).
Public data
The public data set is intended for easier debugging and approximate program correctness checking. The public data set is stored also in the upload system and each time a student submits a solution it is run on the public dataset and the program output to stdout and stderr is available to him/her.
Link to public data set